sources: Cabridge Lower Secondary Science Stage 9- Student’s Book, Our lovely science teacher<3

Chemical Structures and Properties
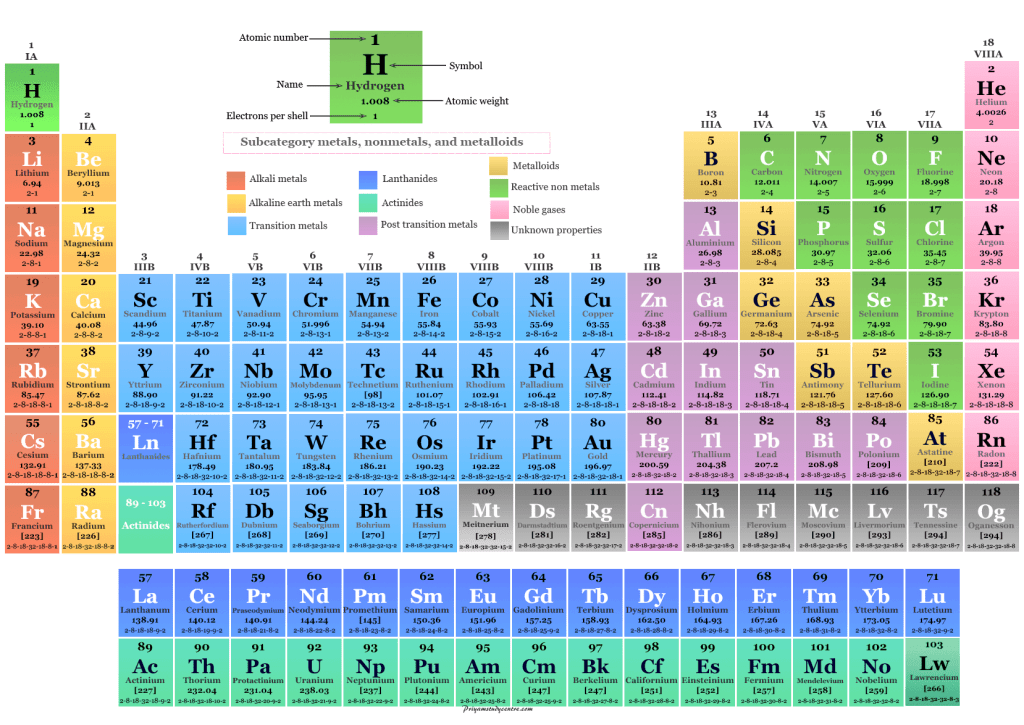
Periodic Table– How the elements are arranged in order of their atomic number
Group– Column in the Periodic Table
Period– Row in the Periodic Table

Chemical Peoperty– A property that is seen when a substance takes part in a chemical change
Physical Property– The property that can be observed or measured without changing the basic nature of the substance
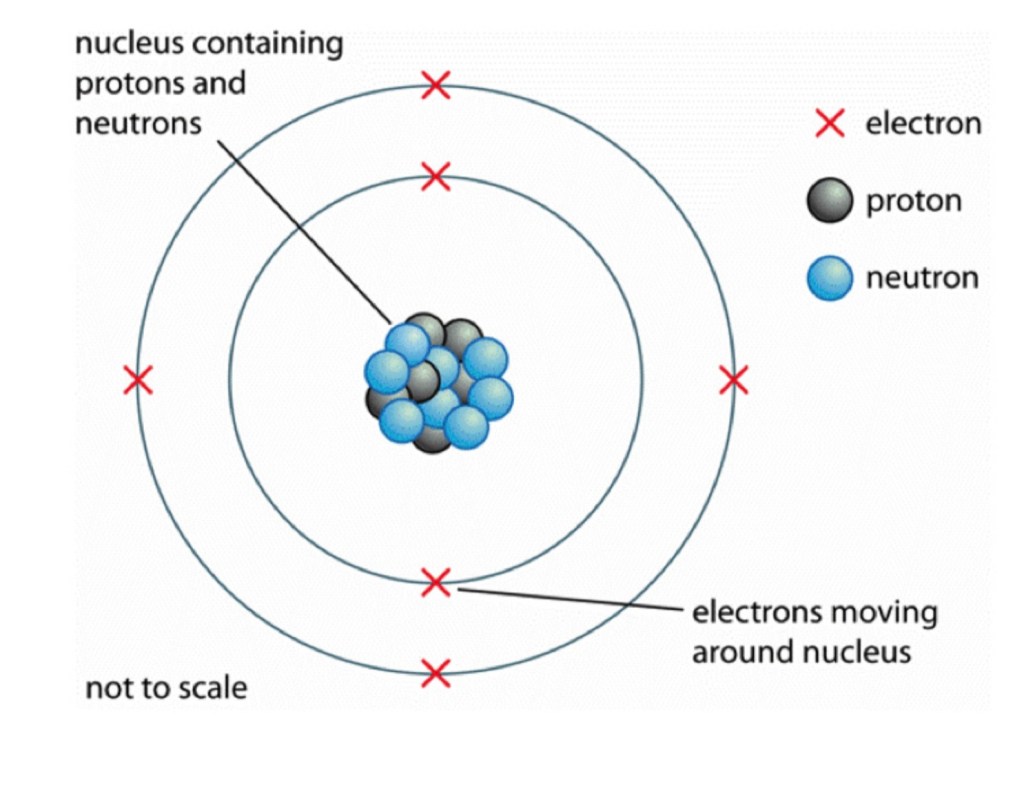
Electrons– Very small negatively charged particles in an atom
Protons– Positively charged particles in the nucleus of an atom
Neutrons– Particles with no charge in the nucleus of an atom
Nucleus– The cetral part of an atom- contains protons and neutrons
Shells– The paths or orbits that electrons move along in an atom
Element Numbers
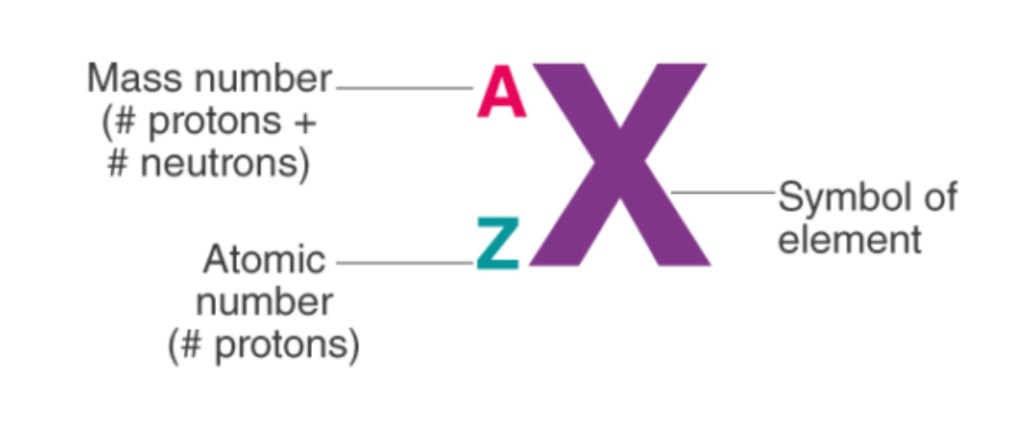
Atomic Number: The number of protons an atom of an element has
Mass Number: The total number of protons and neutrons an atom of an element has. This is the total number of particles in the nucleus
Electron Shells
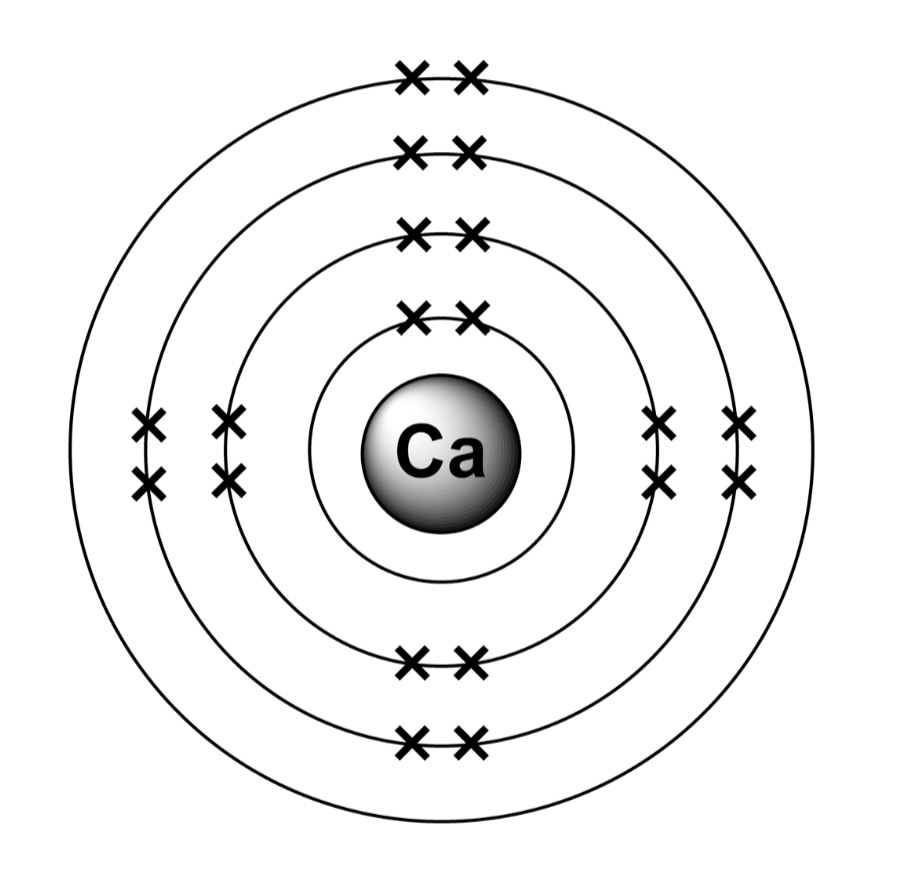
Electrons are arranged in shells around the nucleus.
First shell holds two electrons, second, third, fourth (and so on) shells all hold eight electrons.
Trends in Group 1
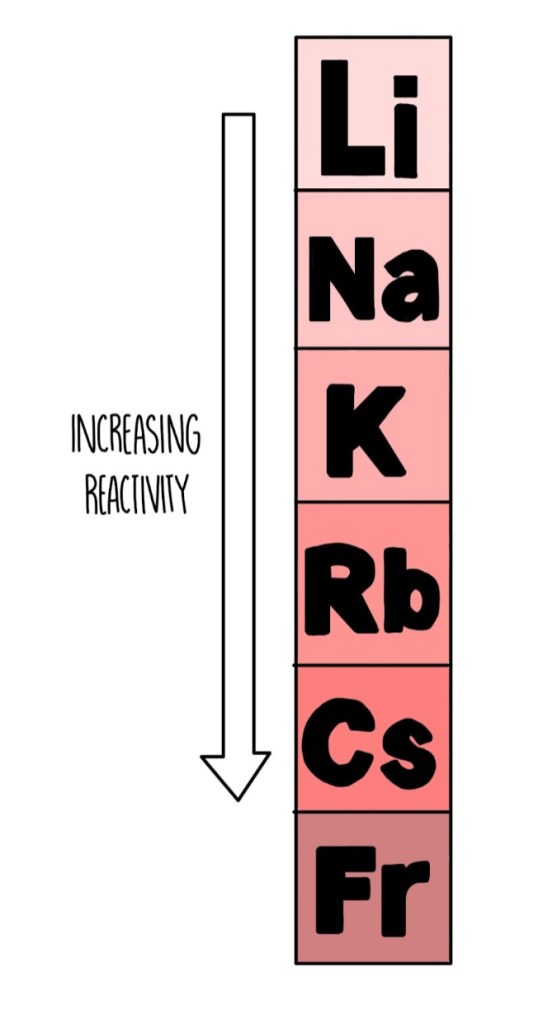
As you gown down, the alkali metals become more reactive
What is a molecule?
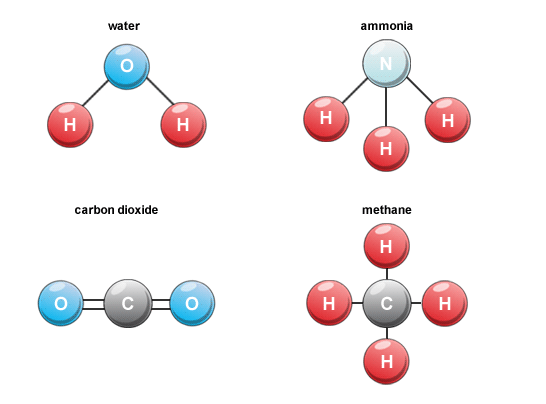
- All substances are made up of particles
- The particles in some subtances are atoms
- Molecules are group or two or more atoms, joined together
- The atoms in a molecule could be the same or they could be different
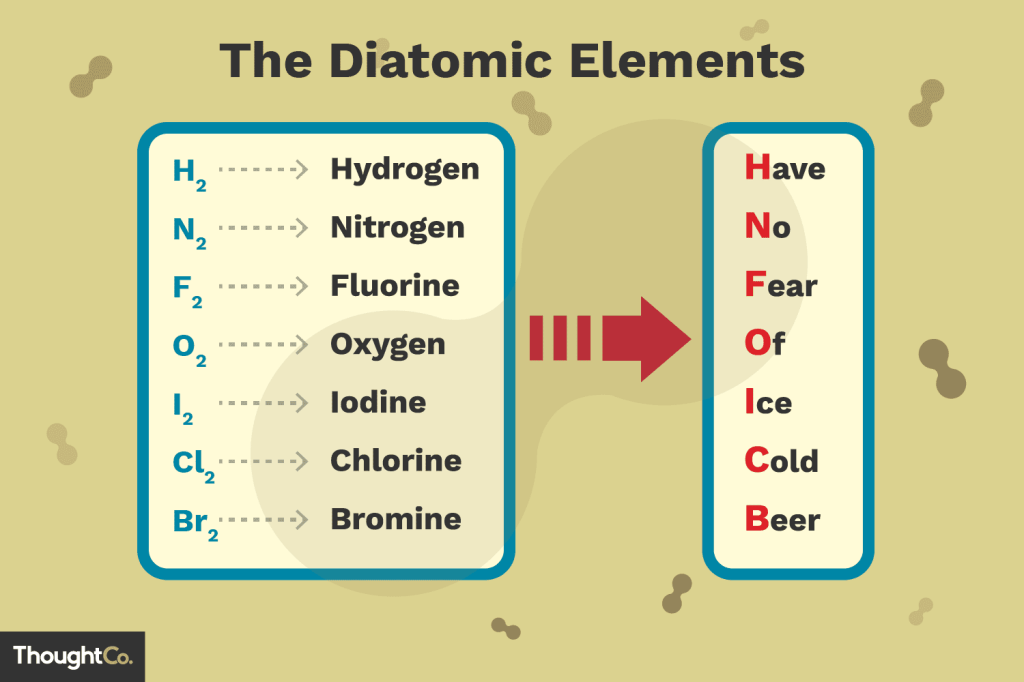
Diatomic Elements
Diatomic Elements are atoms that are never found on their own. They form a bond with another atom of their same type.
Covalent Bonds
- Two non-metals share a pair od electrons in their outer shell
- This makes a full outer shell for all atoms involved
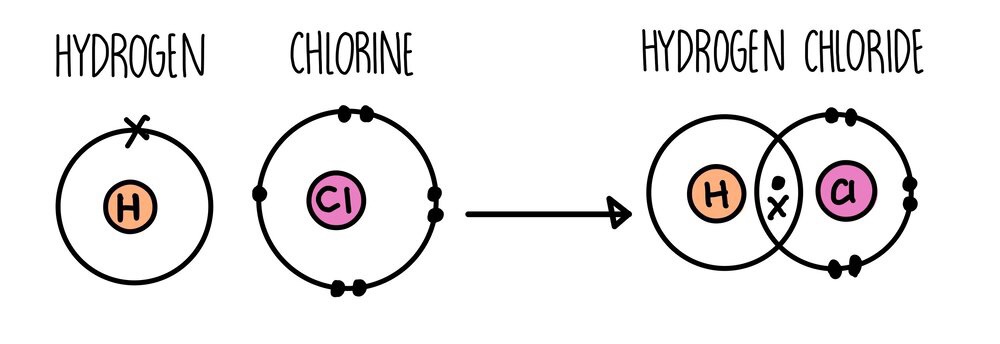
Why does a covalent bond from?
Electrostatic attraction between positevely-charged nucleus of both atoms and the shares negatively-charged electrons.
Ionic Bonds
How is an ion formed?
- During a chemical reaction
- When an atom gains or loses an electron
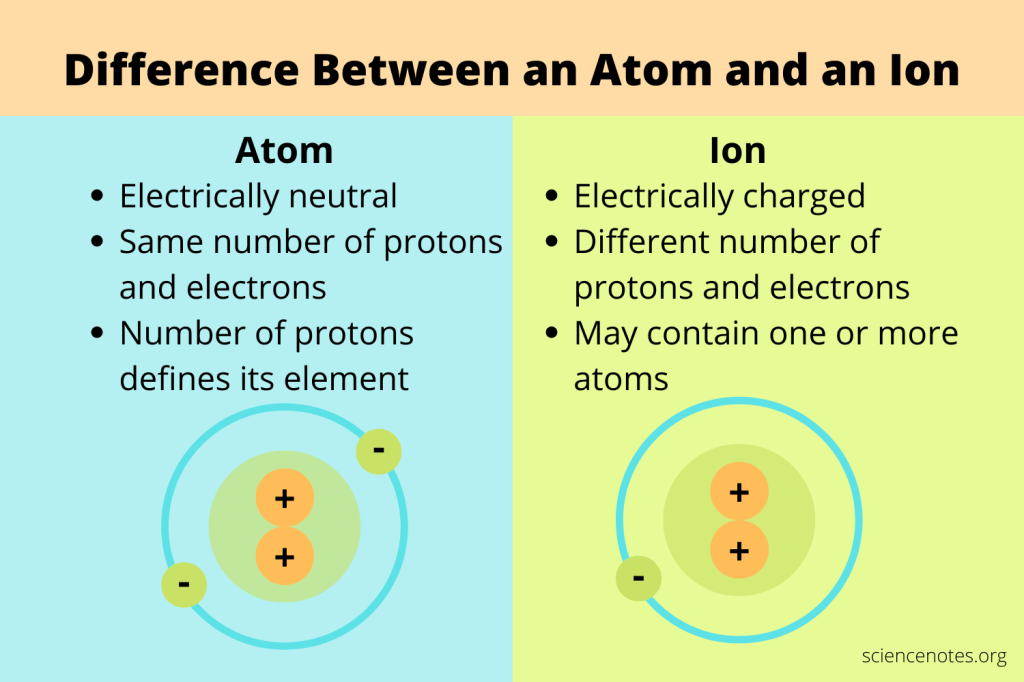
Metals vs Nonmetals
METALS

NON METALS

Non metals gain electrons that the metals transfer to form positive ions.
Giant Structures
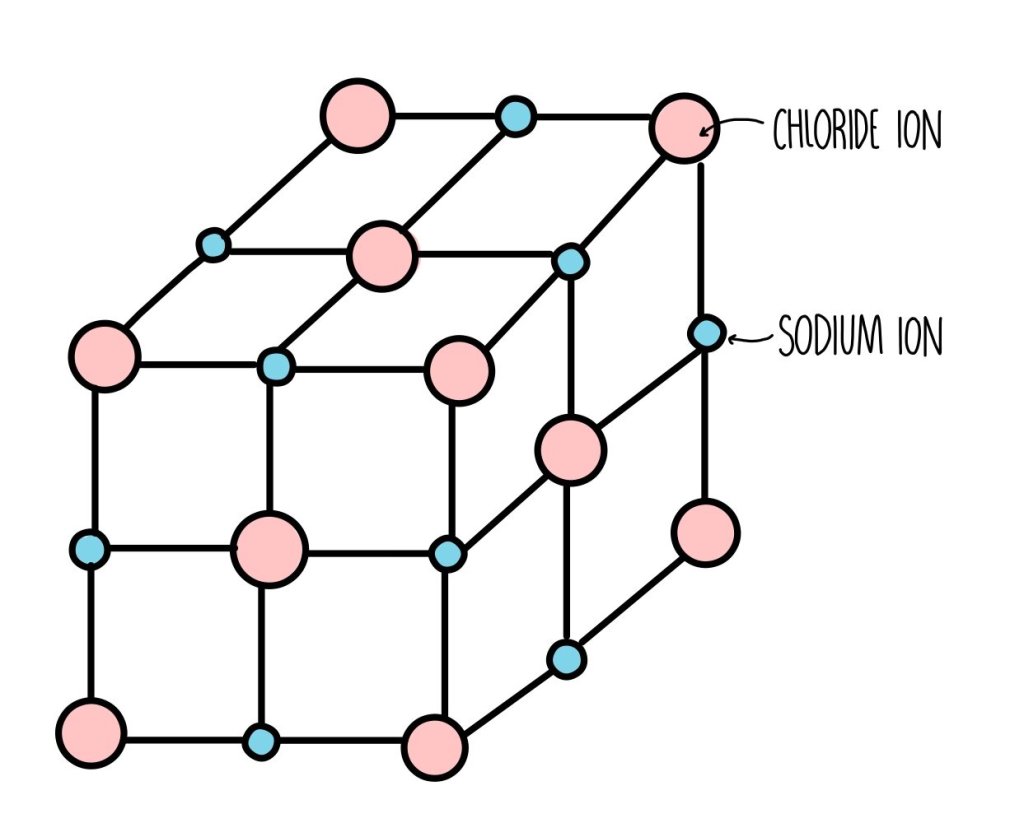
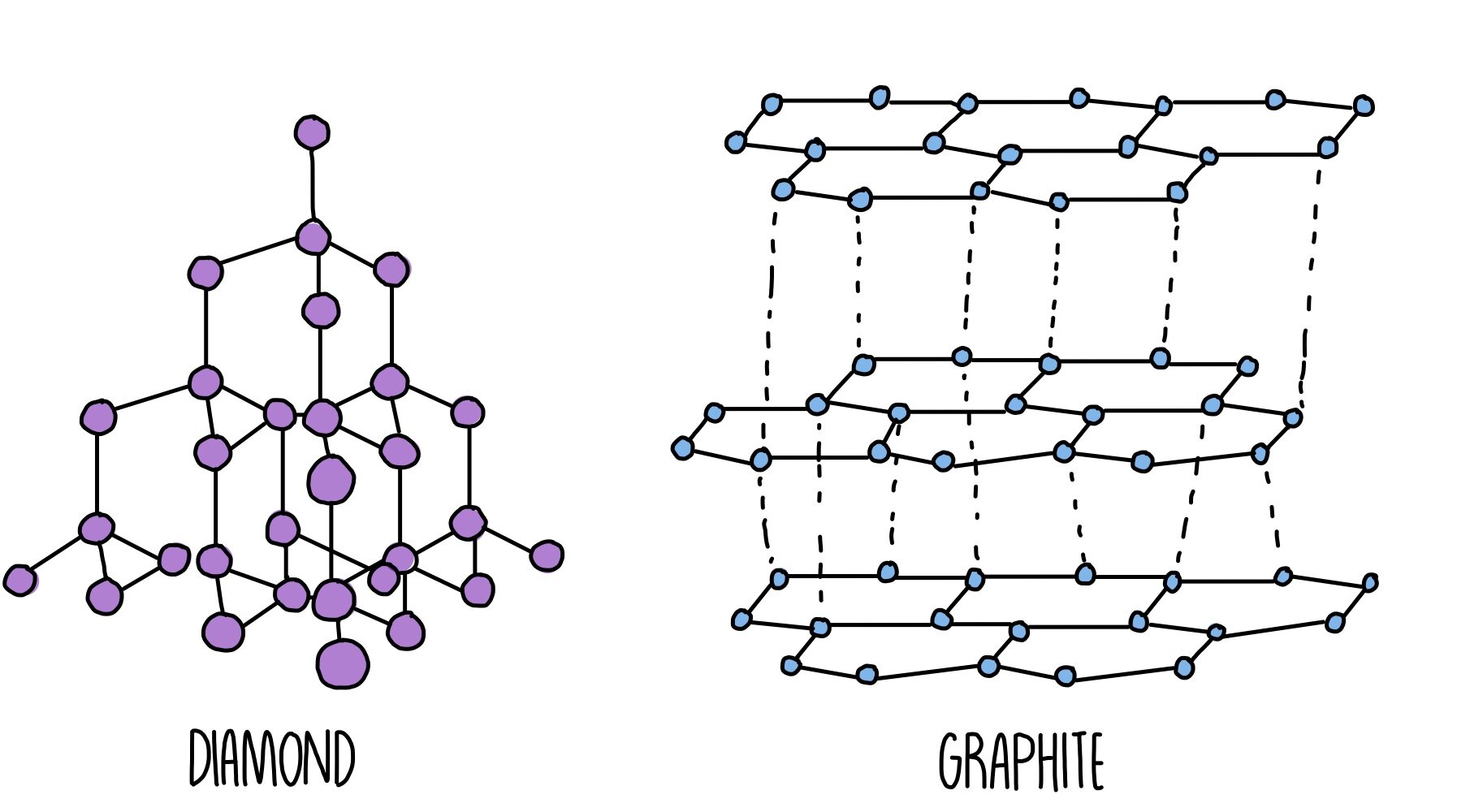
- Very strong bonds exist between each atom or ion.
- Sodium chloride is an example of a compound with a giant sructure. It is made up of positive sodium ions and negative chloride ions.
- Diamond is an element – it only contains carbon atoms. There are four covalent bonds between each element. Diamond also has a giant structure called a giant covalent structure.
- Metals also have a giant structure. They are made up of positive metal ions surrounded by electrons. The electrostatic attraction between the positive ions and electrons are strong metallic bonds. The electrons are able to move. This is why metals can conduct electricity.
- Giant structures have high melting points (and boiling points), and they are usually solids in room temperature.
Simple Structures
- Simple structure is an element or compound that is made up of molecules.
- Very strong covalent bonds hold the atoms in the molecules together.
- Weaker attractive forces exist between the molecules.
- Substances with simple structures have low melting and boilling points. Many exist as liquids or gases at room temperature.
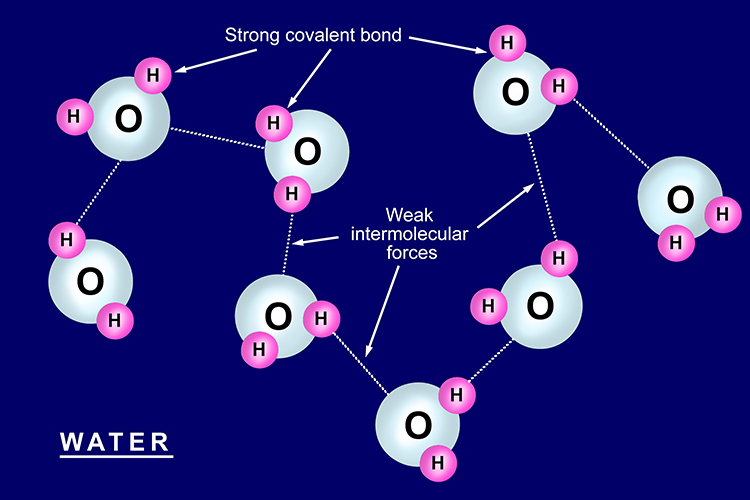
Water is an example of a compound with a simple structure. It contains watefr molecules (H2O). When water is solid (ice) the molecules are held together by weak attractive forces.