sources: Cambridge Lower Secondary Science Stage 9 – Student’s Book, Our lovely science teacher ❤

Changes in chemical reactions

Theory is a set of ideas that explain an observation, (ex. Conservation of Mass, Gravity, Evolution)
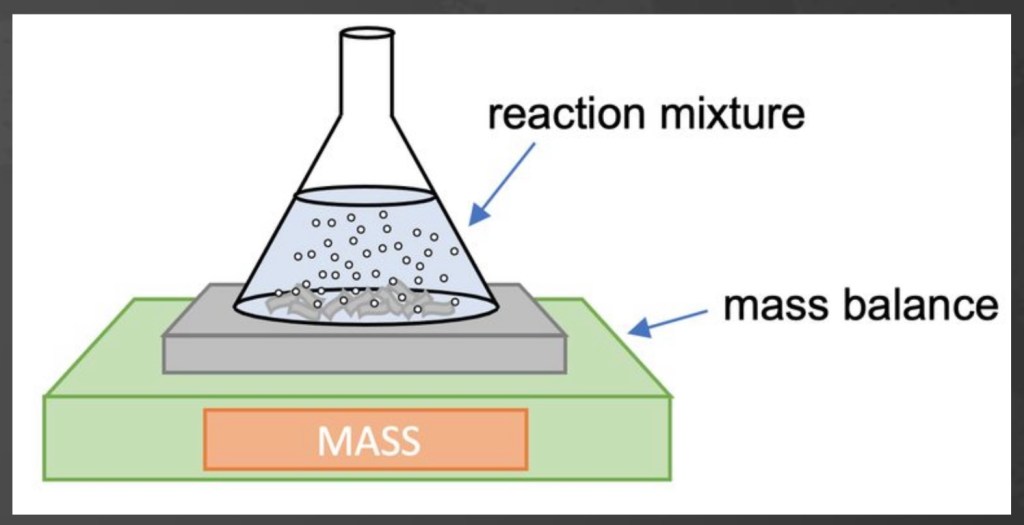
Conservation of Mass
- Matter cannot be created or destroyed
- The mass of products in a chemical reaction equals the mass of reactants
Conservation of Energy
- Energy is stored in chemical bonds of reactants
- During chemical reactions, energy is transferred to the bonds in the products
- Some energy can be transferred to the surroundings
- Energy cannot be created or destroyed

Combustion is a chemical reaction between a substance and oxygen, which transfers energy as heat and light
Word and symbol equations
Word equations
A word equation is a model showing what happens in a chemical reaction, with reactants on the left and products on the right.
- product: substance made during a chemical reaction
- reactant: substance that changes in a chemical reaction to form products
Symbol equations
A symbol equations is a way if showing a chemical reaction using formulae – a balanced symbol equation has equal numbers of each type of atom on both sides of the equation.
- formula: shows the chemical symbols of elements in a compound, and how many of each type of atom there are
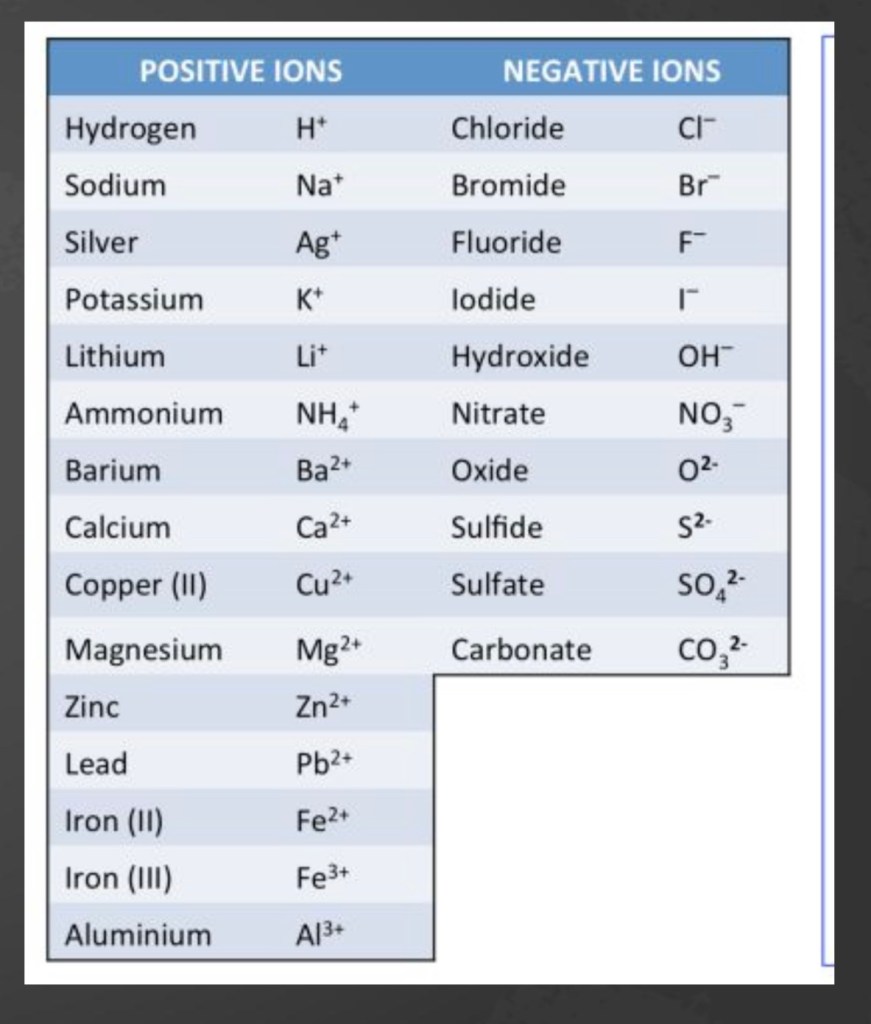
Writing formulae
Methods for making salts
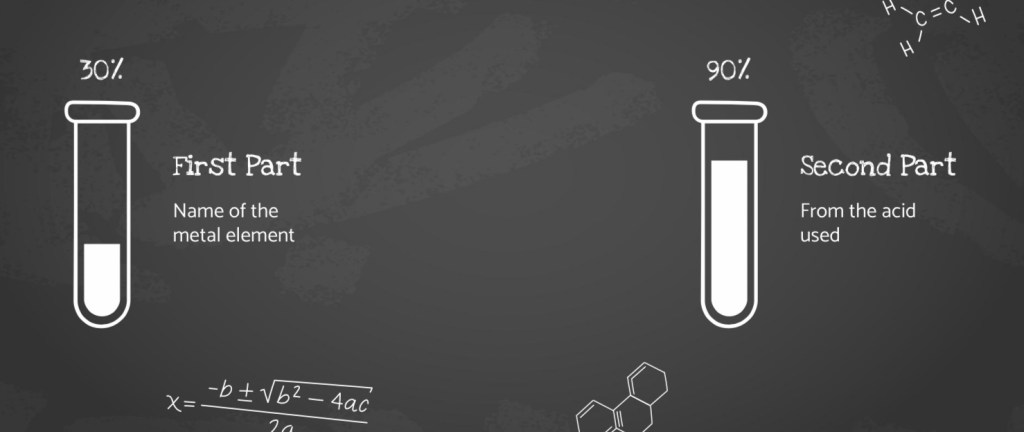
SALTS
Formed when metals and metal carbonates react with acids
THE ACID
Determines the type of salt made
Naming Salts
Reactions between acids and carbonates
- Metal Carbonates: are bases and neutralize acids
- Soluble Bases: known as alkalis and form alkaline solutions
- Products: metal carbonates react with acids to produce a salt, water, and carbon dioxide
Performing the reaction
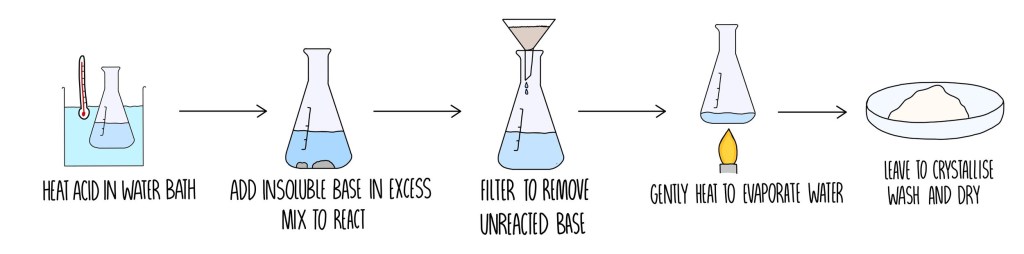
1. Making a soluble salt
First, pour some dilute acid into a beaker. Then add a spatula of the metal or solid metal and stir. Don’t forget about eye protection!
2. Purifying the salt
You will now have a mizture of a salt solution and solid. To purify the salt, the other substances need to be removed.
3. Using filtration

You remove the solid by filtering the mixture. The excess or unreacted solid stays in the filter paper. The salt solution goes through the filter paper and collects in the container below.
4. Using evaporation
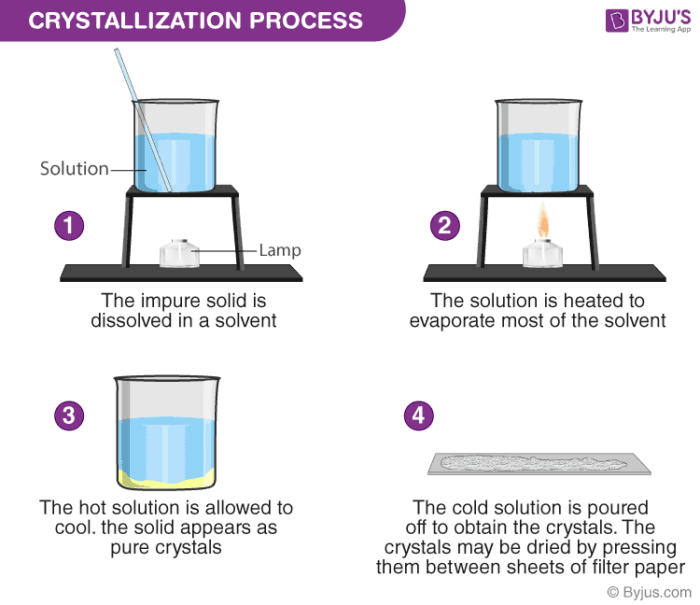
The final step is to remove the water from the salt solution by evaporation. Because this process forms the salt crystals it is called crystallization.
Displacment reactions
What is a displacment reaction?
- The more reactive element will take the place of a less reactive element
- Metals and non-metals can take part in displacement reactions
- Using displacement reactions, you can determine how reactive different metals are
The Reactivity Series
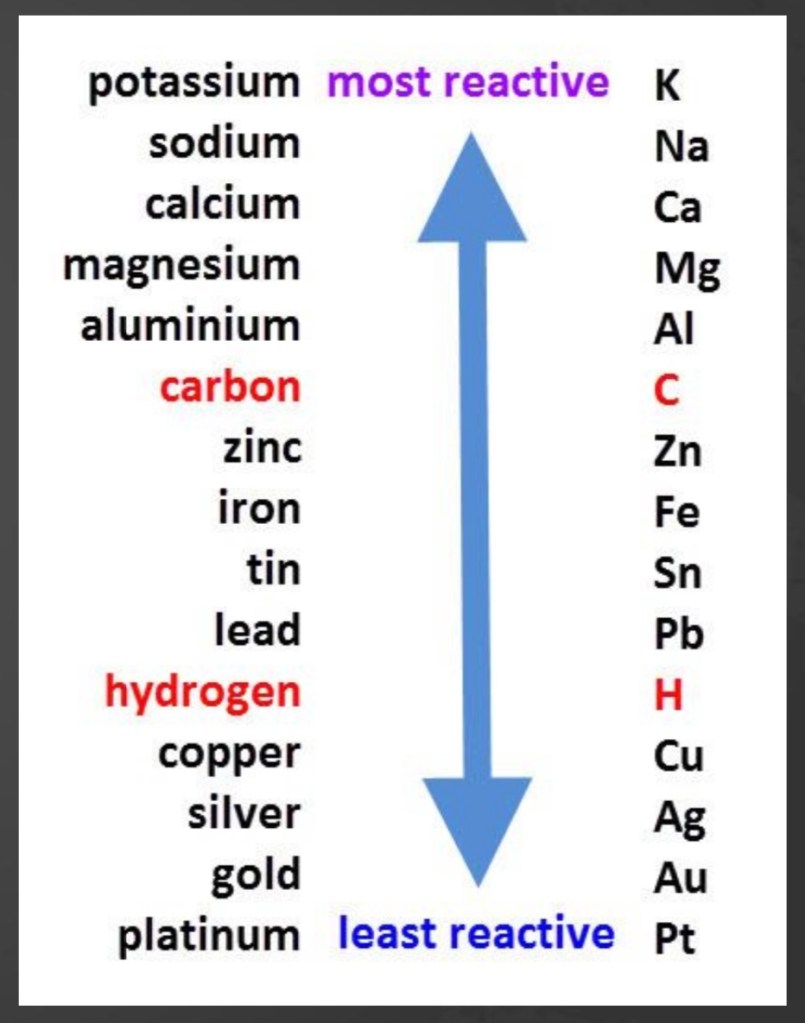
The reactivity series lists metals in order of their relative reactivity.
You can use the reactivity series to predict whether displacment reactions will happen and, if so, what the products will be.
Rates of reaction
How can you compare rates of reaction?
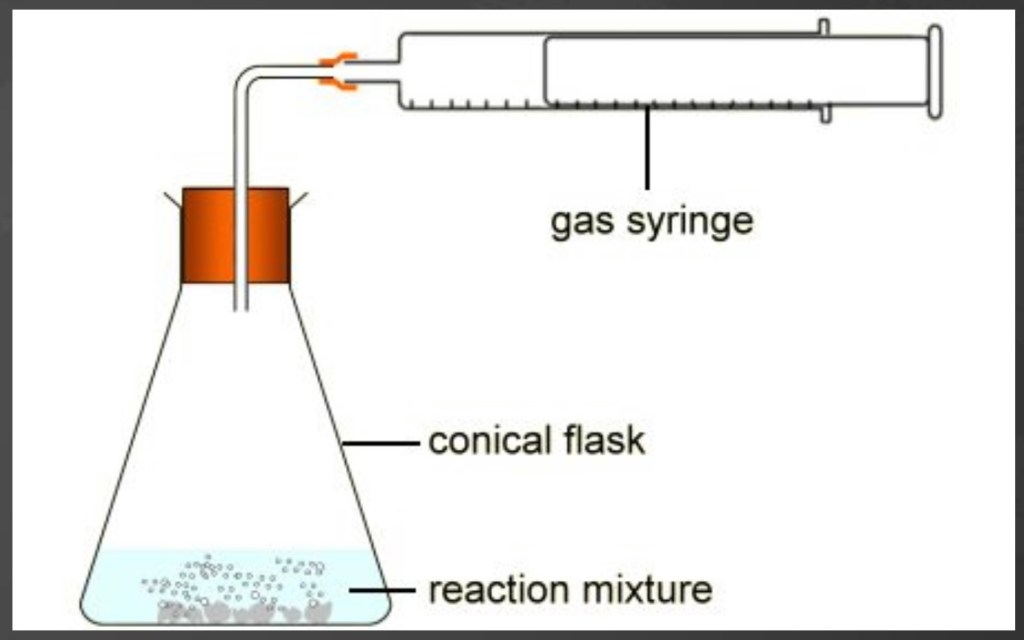
A rate of reaction is the speed at which a reaction happens. This can be compared in different ways – for example, you can measure how quickly a reactant is used up or how quickly a product is made. If a chemical reaction produces a gas, you can measure how quickly that gas escapes from an open container.
Changing the rate of reaction
For a chemical reaction to happen, the reactant particles have to collide with each other. To speed up a chemical reaction, particles have to collide with each other more often or they have to collide with more energy.
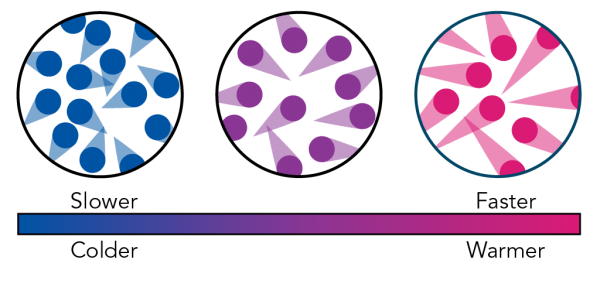
How does temperature impact the reaction rate?
- Temperature is a measure of energy
- Higher energy results in more collisions between particles
- When particles collide with the right amount of energy, they cause a reaction
- Higher temperature results in more collisions, which results in a higher rate of reaction
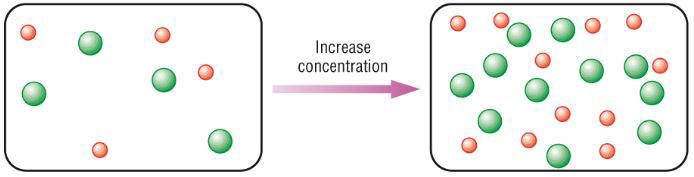
How does concentration impact the rate of reaction?
- Number of particles of a substance in a given volume is concentration
- More particles result in a higher concentration
- If there are more particles, they are more likely to collide and react
- More concentration results in more collisions, which results in a higher rate of reaction
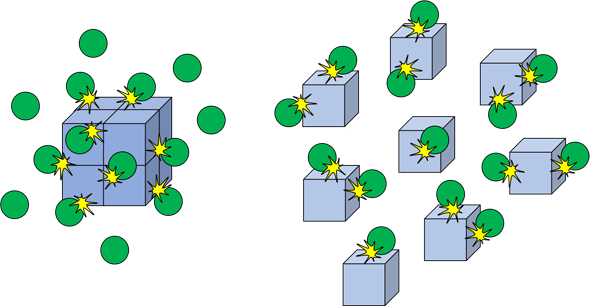
How does surface are impact the rate of reaction?
- The bigger the piece of solid, the slower it will react
- If you break it into smaller pieces, it will react faster because you increse its surface area